- What is Thermal Transfer Ribbon (TTR)?
- What is Thermal Transfer Overprint (TTO)?
- Layers in TTR
- Structure in TTR
- TTR Printing Technology
- Direct Thermal and Thermal Transfer Printing
- The Difference Between Four Printing Technologies
- Why Coding and Marking are so Important for Your Business?
What is Thermal Transfer Ribbon (TTR)?
Thermal Transfer Ribbons is a roll of clear plastic (PE) film with one side being ink coated. It is also known as barcode ribbon, as it often used for printing barcodes onto price tags.
When placed inside the thermal printer, the ink is transferred by heat, forming text or images onto the label.
What is Thermal Transfer Printing?
In Thermal Transfer printers, the image appears when a substrate and ink ribbon contact a heated print-head. The heat from the print-head melts the ink on the ribbon and releases (transfers) the ink directly onto the substrate.
Why Thermal Transfer Printing?

Thermal Transfer printing is a proven technique to deliver variable codes, such as barcodes, that always read or scan. It produces dense, high resolution images colour or black and white, and can be used on a wide variety of substrates. Thermal Transfer printing uses ribbon as transfer-agent. Thermal Transfer images are highly resistant to chemicals and extremely durable. The printers work at high speeds and require little maintenance.
What is Thermal Transfer Overprint (TTO)?
Most application in flexible packaging for high speed printing and packing.
Thermal Transfer Overprint (TTO) is a method where heat is used to transfer ink from a Thermal Transfer Ribbon onto a flexible substrate like food and beverage or pharmaceutical packaging. This technique is used for example for the printing of barcodes and variable information such as best by dates and serial numbers.
For in-line printing Thermal Transfer Overprint, TTO at high speed, Wax Resin Ribbons are the obvious choice.
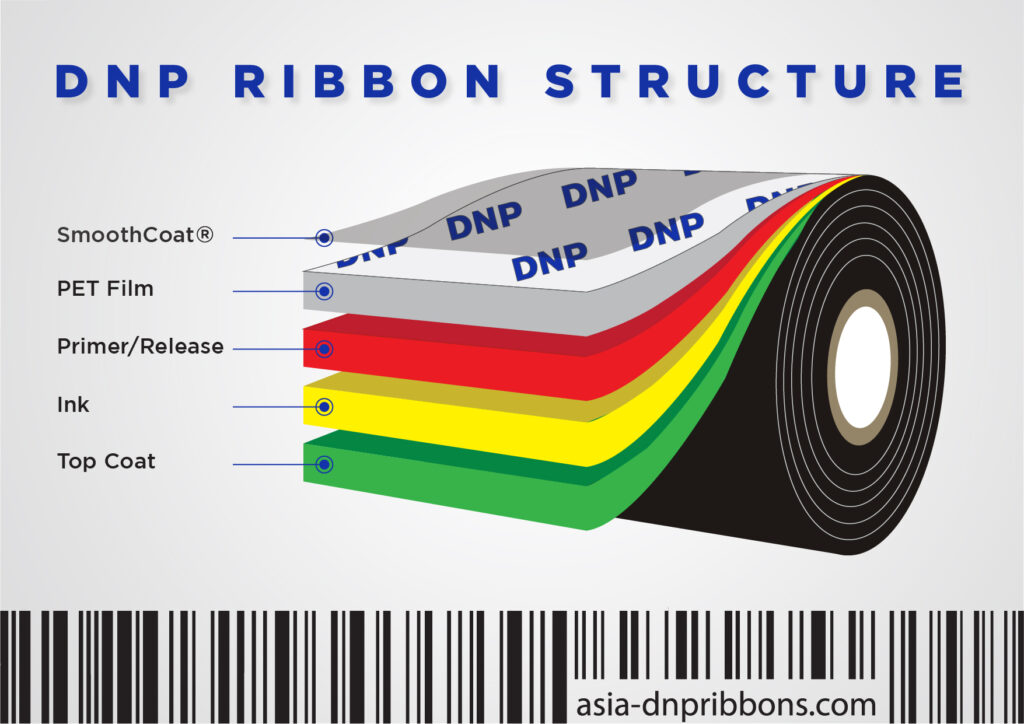
Layers of Thermal Transfer Ribbon (TTR)
Top Coat
Added to DNP's resin ribbons, this is specially formulated to promote adhesion to certain types of label stock.
Ink
This provides the printed image, and can contain wax, resin, or a mixture of the two.
Primer (Release Layer)
This acts to bond the ink to the PET film during the coating process and promotes transfer of the ink to the label during the printing process.
PET Film
This polyester film is the "carrier" for the ink, adhesive layer, and the backcoat. Essentially, the chemical layers that make up the ribbon are all applied to this base film. A thin film for all the layers to rest on.
Backcoat
The backcoat is a specially formulated chemical coating that protects the printhead from the ribbon during the thermal transfer printing process. It comes into contact with the printhead and provides smooth travel and excellent heat transfer.
Structure of Thermal Transfer Ribbon (TTR)
Paper/Plastic Cores
Ribbons are usually wound on Paper/Plastic cores. These cores must be manufactured, prepared, and stored carefully to optimize the quality of the ribbon rewind during manufacturing and to maintain the quality of the ribbon during use.
Leader Tape
This protects the ribbon during shipping and facilitates the loading of the ribbon into the printer.
Ink
Ribbon can be a lot of colours.
Trailer Tape (Ending Tape)
TTR Printers have optical sensors to shut the printer off when the end of the ribbon is reached.
TTR Printing Technology
There are two different printerhead technologies – Flat Head and Near Edge.
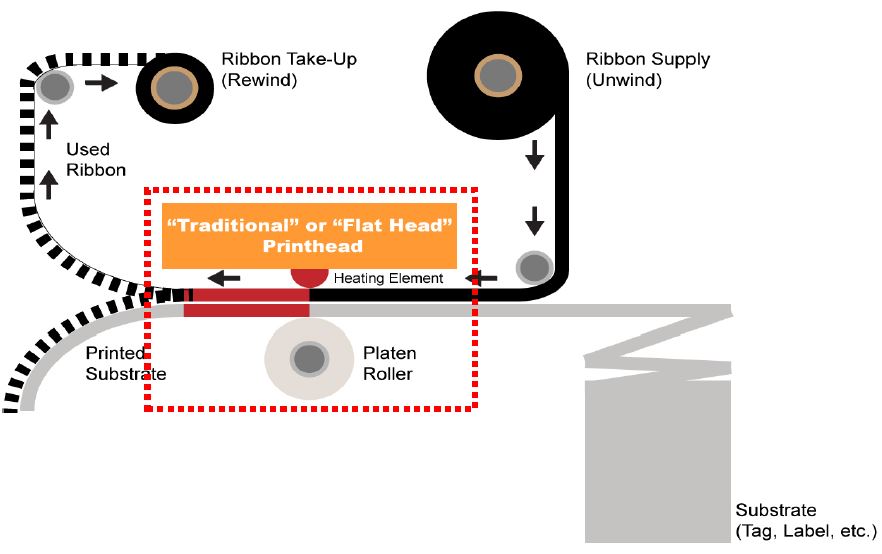
Flat Head Printer Technology
Printers with a traditional printhead that allow for the ribbon and substrate to bond for a short distance till the peel point after passing the heating element.
Flat head printers have a traditional print head that can provide image resolutions from 203 to 600 dots per inch (DPI). Their ribbons are married with labels for a small distance to the peel point after passing the heating element.
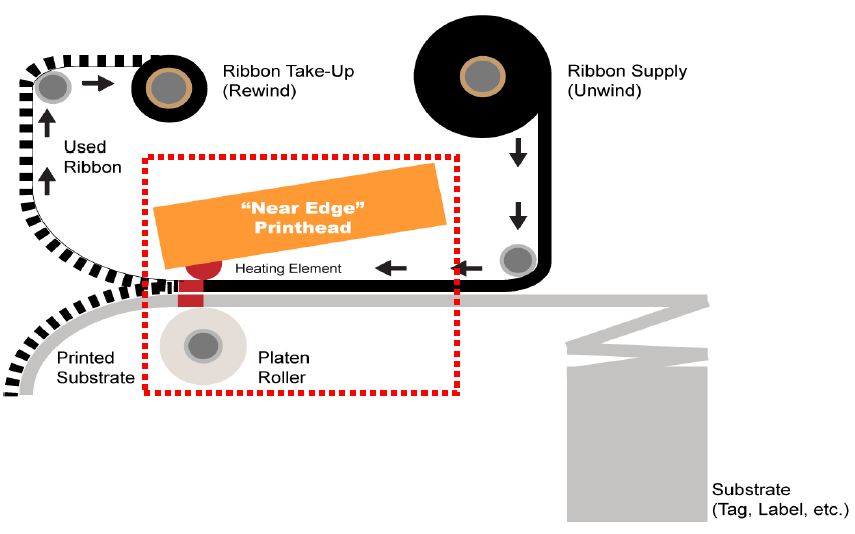
Near Edge Printer Technology
Printers with an angled printhead, where the substrate and ribbon separate almost immediately, allowing for a faster printing process.
Near edge printers with their floating print heads will run more than twice as fast at speeds over 32 IPS. Ribbons for these printers are married with labels only for an instant prior to the peel point, requiring a special formulation engineered for quick release of ink from the PET film.
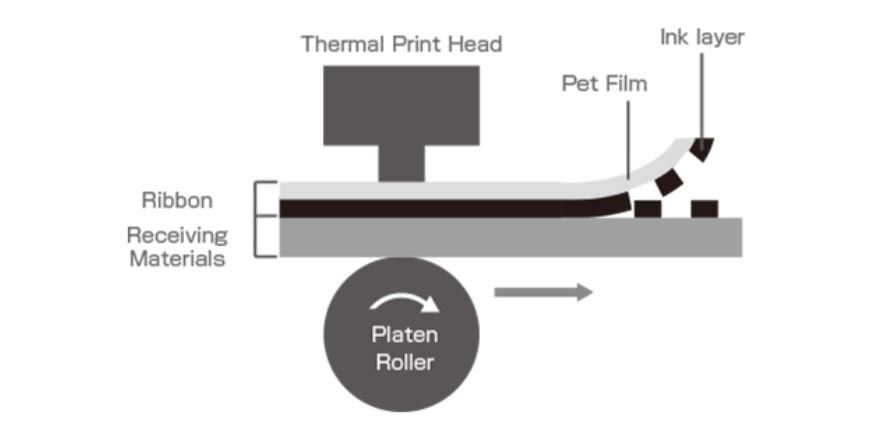
Thermal Transfer Ribbon System
Thermal Transfer Ribbon film is coated on a thin film with wax ink evenly. The coated film is used for barcode printing.
The wax ink is mixed with carbon & color pigments and coated several micron thickness on to a three to six micron thickness film. When heat is transferred via thermal print head on to the film, the heated area alone melts and the ink is transferred to the paper.

What is the Difference Between Direct Thermal Printing and Thermal Transfer Printing?
The main difference between Direct Thermal Printing and Thermal Transfer Printing is the durability of the printed image and the consumables used for the concerning technologies.
With direct thermal printing a thermal paper is used, which is suitable for variable printing when heat is applied to the paper. Whereas with Thermal Transfer Printing, both a substrate e.g. paper, PET, PP etc. and a Thermal Transfer Ribbon are used to print variable information. Due to it’s resistance capabilities, direct thermal transfer is often used for product identification where the variable code is not exposed to harsh chemicals, light or extreme temperatures.
The Difference Between Four Printing Technologies
Thermal Transfer Overprinters (TTO)
Characteristic: Clear black and information distinct
These machines are ideal for solvent-free coding and cost-effective with few consumables. It can function effectively in either fast-moving or intermittent manufacturing processes. The TTO distinct design delivers a straightforward and user-friendly operation.
This machine is ideal for date coding on various substrates, including plastic films, flat packaging, corrugated boxes, cutlery, and other food-safe materials.
Thermal Inkjet Printing
Characteristic: Information and numbers are formed with black circular dots
The jam jar is labeled and the expiry date is printed on the metal lid or on the glass using a durable thermal inkjet printer. Thermal inkjet printers can also be integrated on a film machine, sleeve or carton feeder.
Thermal inkjet printers are less polluting than the common continuous inkjet printers, making them a sustainable and environment-friendly solution. This also allows for your investment to be quickly recovered.
Stamping Printing
Characteristic: Information and numbers are printed with indistinct concave effects
Hot Stamping Printer are widely used to print product date, shelf life, weight in the industry of Food & Beverage, Pharmaceutical, Health & Beauty, Electronic Components, Chemicals and others.
It can print clearly on all kinds of plastic film, composite film bags, and plastic and other flexible packaging products.
Laser Marking Printing
Characteristic: Information and numbers are printed with distinct and precise concave effects
These date coding machines are one of the most reliable, versatile, and cost-effective marking technologies available. They provide indelible marks for the most highly regulated industries and ones with strict dimensional standards.
Laser coders are a fantastic selection for high-speed date stamping because they are precise.
Get to Know First About Coding and Marking
Coding refers to the process of creating and applying codes that contain specific information about the product. These codes can be alphanumeric, barcodes, QR, or other machine-readable symbols.
Marking is the physical process of applying the code onto the product or packaging. It can be done through various technologies such as inkjet printing, laser marking, thermal transfer, or labeling.
These codes serve various purposes, from tracking and tracing to compliance and branding. Moreover, codes can be used to verify the authenticity of products, protecting against counterfeiting and fraud.

Why Coding and Marking are so Important for Your Business?
1. Ensuring Traceability and Compliance
Proper labeling with identifying information ensures traceability throughout the supply chain. This traceability is vital for tracking products from manufacturing to distribution, allowing quick response to any issues or recalls. Compliance with industry regulations is also maintained through accurate coding and marking, helping manufacturers avoid costly penalties and legal challenges.
2. Improving Production Efficiency and Reducing Waste
Automation in coding and marking minimizes human error, leading to a more efficient production process. Waste is minimized by reducing mix-ups in production through correct labeling, leading to cost savings and a more sustainable operation.
3. Enhancing Product Security and Authenticity
High-quality codes and symbols ensure that products are genuine and untampered, protecting consumers and brands. This security is vital in many industries where counterfeit products pose significant safety risks.
4. Enhancing Supply Chain Visibility
Proper labeling improves supply chain visibility, making tracking products and identifying potential issues or bottlenecks easier. This visibility allows for real-time adjustments and optimization, enhancing overall supply chain efficiency.
What is a Barcode?
A barcode is a pattern that consists of parallel lines of different widths. These bars are for entering data into a system. Barcode is black on a white background and the width of a code may vary depending on the type of application.
The barcode can be adjusted to the user’s requirements. It’s possible to have simple and complex information represented in a barcode. The bar or white spaces of a particular width in a certain position is read by a barcode reader and transferred to the computer as a 0 or 1.
For some barcodes, there are two different bar widths, while for other codes up to four widths can be applied. The numbers that are printed at the base of a barcode are the ones represented by this barcode.
What is a QR code?
QR codes are two-dimensional matrix barcodes that you can instantly scan with your phone. It’s an advanced version of a barcode that comes with a variety of benefits. Due to that, they can be read by scanners both horizontally and vertically. A QR code has a complex structure. It usually comes in a square shape with black and white squares and dots.
This complex structure gives a great advantage to QR codes over barcodes, as they have better information capacity and are more error-tolerant. The flexibility that QR codes provide makes them perfect for businesses that want to use codes for marketing campaigns or other ways for engagement with customers.
QR codes are most commonly used to link a company’s websites or social media accounts. However, there are many more ways QR codes can be used for a business. QR codes can store up to 4296 characters with punctuation and special characters, making it easy to encode website URLs.
Types of Coding and Marking Systems
- Continuous Inkjet Printer (CIJ), Laser Marking, Piezo Inkjet Printers, Thermal Inkjet Printers (TIJ), Thermal Transfer Overprinters (TTO)